- Home
- Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC)
Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC)
Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC)
Liver Illness
At a glance
- PBC predominantly affects middle-aged women
- Symptoms are comparable with many liver diseases including fatigue, pruritis and jaundice
- Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and slowing disease progression
- Click here to read Carol Ann’s story with PBC
What is it?
Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) is a chronic liver disease characterised by progressive inflammation and destruction of the bile ducts. This auto-immune disorder leads to bile accumulation and liver damage over time.
Symptoms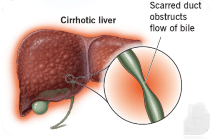
Typical symptoms include fatigue, pruritus (itchy skin), jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and xanthomas (fatty deposits under the skin).
Incidence
The disease predominantly affects middle-aged women, with the average age of diagnosis being around 50 years. In Ireland, PBC has an incidence rate of approximately 1 in 1,000 women over the age of 40.
Treatment
Treatment options focus on managing symptoms and slowing disease progression. Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is commonly prescribed to improve liver function. In advanced cases, liver transplantation may be necessary.
Prognosis
The prognosis for PBC varies. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve quality of life and delay progression. However, without intervention, PBC can lead to cirrhosis and liver failure.
References
- Mayo Clinic. Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC). Mayo Clinic
- Irish Liver Foundation. Understanding PBC. Irish Liver Foundation
